Electrochemical CO2 reduction method
High-efficiency CO2 electroreduction under hydrothermal conditions
Overview
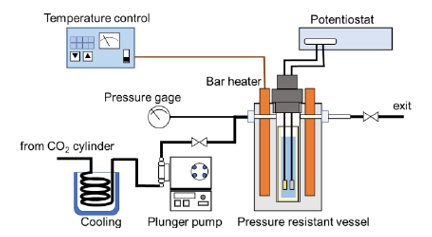
The electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction (CO2RR) process, in which CO2 is electrochemically converted, is attracting attention as a promising CO2 reduction method. However, the conventional method has a problem of low energy efficiency. The inventor has found that it is possible to improve the efficiency of the CO2RR process by utilizing a high-temperature high-pressure water environment called a hydrothermal conditions. When electrolysis is carried out in high-temperature high-pressure water at 150℃ and 100 atm pressurized with CO2, the high diffusion coefficient and solubility of CO2 in the water facilitating efficient CO2 supply to the electrode, and the energy efficiency is significantly enhanced. Additional assessment has shown that it is possible to synthesize "carbon-negative" basic chemical product (methanol), in which the amount of CO2 absorbed exceeds the amount of CO2 emitted, by leveraging low-temperature waste heat from industrial sources and renewable electricity.
Effect of hydrothermal conditions on current density and products 1
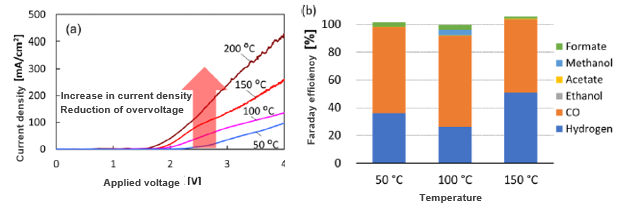
(a) Current density as a function of the applied voltage at various temperatures at 10MPa.
(b) Faraday efficiency (FE) for each compound produced by the cathodic reduction at ≈100 mA cm−2 under hydrothermal conditions (50–150 °C at 10 MPa).
Increasing the temperature enhances current density and enables the reaction to occur at a lower applied voltage, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Product Application
・High‑efficiency CO2 electroreduction using flue gas and low‑temperature waste heat from factories, power plants, and waste‑to‑energy plants
Related Works
[1] Advanced Sustainable Systems, 2024, 2400489
https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202400489
IP Data
IP No. : PCT/JP2025/009449
Inventor : TOMAI Takaaki
keyword : Hydrothermal Reaction, High Temperature, High Pressure, Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Reaction,
CO2RR
