Predictive Markers for the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Discovery of a Correlation Between Blood Levels of a Compound and Post-ICI Survival Time
Overview
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) offer lasting treatment efficacy and improved survival for cancer patients, but positive responses are limited to select individuals and treatment costs are high, highlighting the need to predict benefit before therapy. Current predictive methods like PD-L1 testing mainly measure local tumor tissue expression and fail to fully assess systemic immunity.
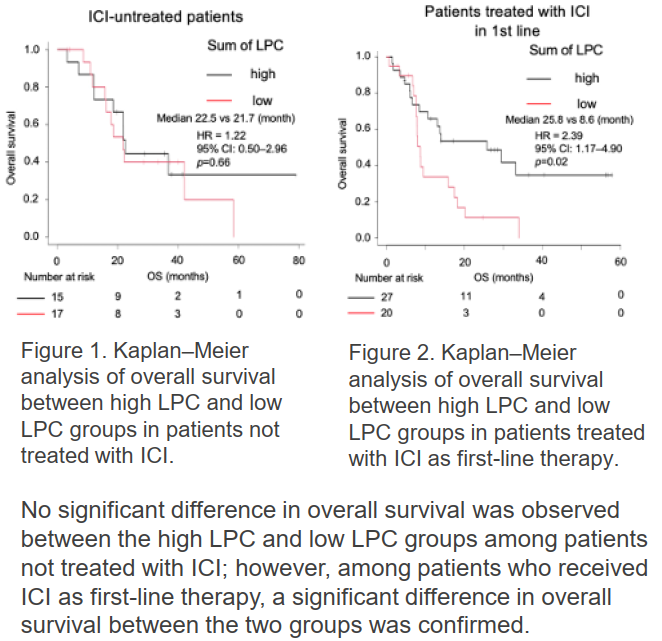
Researchers examined blood lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) levels and clinical outcomes after ICI therapy in squamous cell carcinoma patients. They found that those with higher LPC had significantly prolonged survival post-ICI compared to those with lower levels. Because LPC is measurable in blood samples, it reflects systemic immune status and reduces patient burden by eliminating biopsies. This finding supports developing new clinical tests for predicting ICI effectiveness.
Prolonged Overall Survival After ICI Administration in High LPC Group
Product Application
・Clinical diagnostic reagent for predicting the efficacy of ICI therapy using blood specimens
Related Works
[1]Iwasaki T. et al., Plasma Lysophosphatidylcholine Levels Correlate with Prognosis and Immunotherapy Response in Squamous Cell CarcinomaInt. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 7528 (2025). doi:10.3390/ijms26157528
IP Data
IP No. : JP2025-053633
Inventor : SHIROTA Hidekazu, HISHINUMA Eiji, IWASAKI Tomoyuki
keyword : Immune checkpoint inhibitors, Clinical diagnostic reagents, IVDs, Efficacy prediction
